Docker containers using Ansible on AWS
In the article we will see how to run docker container on target machine using ansible playbook on AWS instance.
Ansible is an open-source configuration management and deployment tool.
Below are the steps to run docker container on AWS EC2 instances using Ansible playbook.
- Create AWS EC2 instances (master and slave)
- Update the security group of slave exposing port 8080
- Install Ansible on master
- Install python on slave
- Update /etc/ansible/hosts on master with the slave IP
- Create a dockerfile which will be used to create customized image
- Create an ansible playbook with detailed tasks
- Execute the ansible playbook
- Check if the docker container is running successfully on the slave machine
Install Ansible on master machine:
Execute the below commands to install Ansible on the master machine:
|
|
Install Python on slave machine:
Use the below commands to install python on the slave machine:
|
|
On the master machine perform the below steps to create ssh-keygen:
|
|
File names id_rsa.pub will be generated after executing ssh-keygen on master machine.
Copy the contents of the id_rsa.pub file and paste it on slave machine inside the authorized_keys file located at /home/ubuntu/.ssh
Update the hosts file on master:
To establish ssh connection with the slave machine, add the IP of the slave machine on master’s hosts file.
To edit the hosts file use the below command:
sudo nano /etc/ansible/hosts
Paste the below content at the end of the file:
|
|
To verify the ssh connection between the master and slave, execute the below command:

Creating the code directory on master machine:
Create a directory named LAMP_STACK_content at /home/ubuntu/ location on the master machine. Create a dockerfile at this location.
Create a dockerfile:
In order to create a customized image we will create a dockerfile with the following contents:
|
|
Create ansible playbook:
Create an ansible-playbook-lamp-stack-new.yaml file on master with the below content.
|
|
Execute the ansible playbook:
Note: Before proceeding ahead with the next steps, you will need to perform docker login using the dockerhub account on the slave machine from where the image will be pushed and pulled.
To execute the playbook use the below command:
ansible-playbook ansible-playbook-lmap-stack-new.yaml

To verify the execution of playbook:
Check if the code directory is copied on the slave machine.
Check if the docker container is running on the slave machine:
docker ps

Note: If you get permission denied error after executing docker ps command then you need to give permissions to the docker.sock file by executing the below command:
chmod -R 0777 /var/run/docker.sock
On the slave machine add the in-bound rules to direct traffic to the port 8080 by updating the security groups on the AWS console as shown below.
Access the slave IP with the exposed port 8080 on the browser and the application should be up.
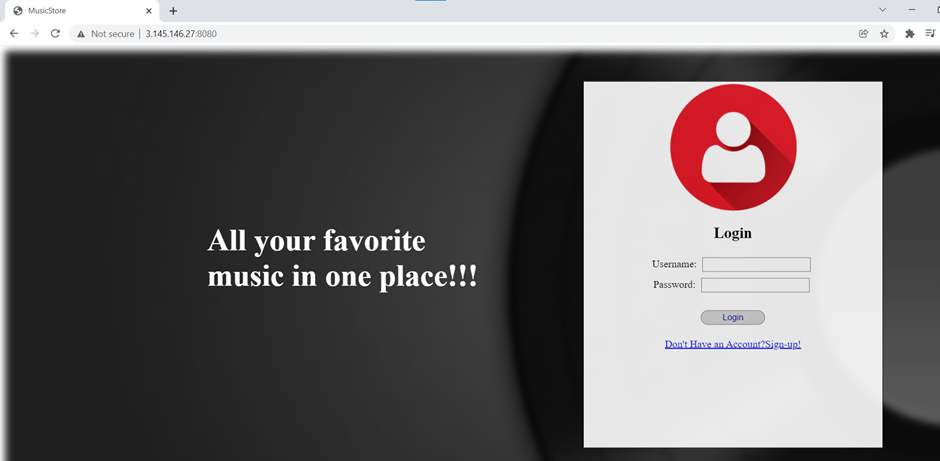
Hope the article was useful, thanks for reading! Happy learning. 👍
Vrinda Hegde is a DevOps Engineer, who likes to explore orchestration tools and automate the process of deploying containerized applications. She likes to share her findings by writing articles on medium.com. She can be reached out on LinkedIn or via email
Siya Amonkar is a DevOps Engineer who likes to explore new tools and technologies. She can be reached out on LinkedIn or via email



